Originating from the thymus, NKT (Natural Killer T) cells represent a combination of T cell and NK cell attributes/markers. They express a T cell receptor (TCR) complex and several NK cell markers. The ability of these cells to produce Th1 and Th2-related cytokines has implicated them in several fields, including transplantation, tumors, autoimmunity, and allergy.
View our: Innate Immunity Pathways

Natural Killer T Cells
Classification
While NKTs display a TCR, the chains displayed are often very limited. This group of NKTs has thus been aptly named invariant NKT cells (iNKT). iNKT cells mostly express the Vα14-Jα18 α chain with a variable Vβ2, Vβ7, or Vβ8.2 chain in mice, while human iNKT cells tend to express Vα24-Jα18/Vβ11. While the iNKTs are the most well-understood class, there are others with semi-variant TCRs or NKT-like features. Some NKT cells express CD4+ or CD8+ individually. Others still are double negative (CD4-, CD8-).
| Type I cells(Classical NKTs) | Type II cells(Non-classical NKTs) | NKT-like cells | |
| CD1d dependent | Yes | Yes | No |
| α-GalCer reactive | Yes | No | No |
| TCRα chain | Vα14-Jα18 (mice); Vα24-Jα18 (humans) | Diverse, but some Vα3.2-Jα 9, Vα8 (mice) | Diverse |
| TCRβ chain | Vβ2, Vβ7, and Vβ8.2 (mice); Vβ11 (humans) | Diverse, but some Vβ8.2 (mice) | Diverse |
| NK1.1 or (CD161) | Positive (resting mature); negative/low (immature or post-activation) | Positive and negative | Positive |
| Subsets | CD4+, DN (mice); CD4+, CD8+, DN (humans) | CD4+ and DN (mice) | CD4+, CD8+, and DN |
| IL-4 production | Yes | Yes | No |
| IFN-γ production | Yes | Yes | Yes |
DN: Double Negative (CD4-CD8-); Adapted from Godfrey, D. et al. 2004. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:231.
To see more NKT cell reagents, click here.
CD1d Restriction
Unlike classical T cells, NKT cells are activated by CD1d and not MHCs. While classical T cells recognize MHC-presented peptides, NKT cells recognize lipids/glycolipids. One of the most famous NKT ligands is called α-galactosylceramide (αGalCer). Originally derived from sea sponges, this compound was found to effectively activate NKT cells. αGalCer also shares structural similarities with components in bacterial cell walls. As such, NKT cells can be potent fighters against bacterial infection.
NKT cells will reciprocally activate its antigen presenting cell upon lipid/glycolipid presentation. Once mature, NKT cells produce massive amounts of IFN-γ. Unique among lymphocytes, they are also capable of explosively releasing IL-4 and IL-13 (Th2-related cytokines). NKT cells burn up fast, downregulating their TCR following activation, and undergoing massive apoptosis once the threat has passed. NKT cell numbers remain deflated until new NKT cells emigrate from the thymus. Because of its ability to promote Th2 cells, NKTs been implicated in Type 1 Diabetes and Asthma.
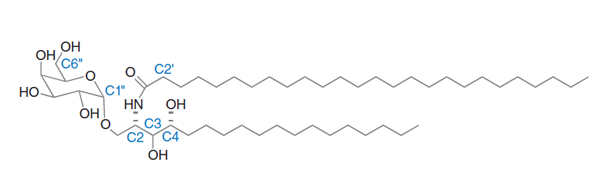
Structure for αGalCer , a popular ligand of NKT cells.
References:
Bendelac, A. et al. 2007. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 25:336.
Development
Like T cells, NKT cells begin their training and development in the thymus. At the double positive (CD4+CD8+) stage, they begin to diverge, undergoing several rounds of division and even acquiring a memory/effector-like phenotype just before they shuttle out of the thymus. NKT cells will then begin to express NK lineage receptors once it heads to its target tissue.
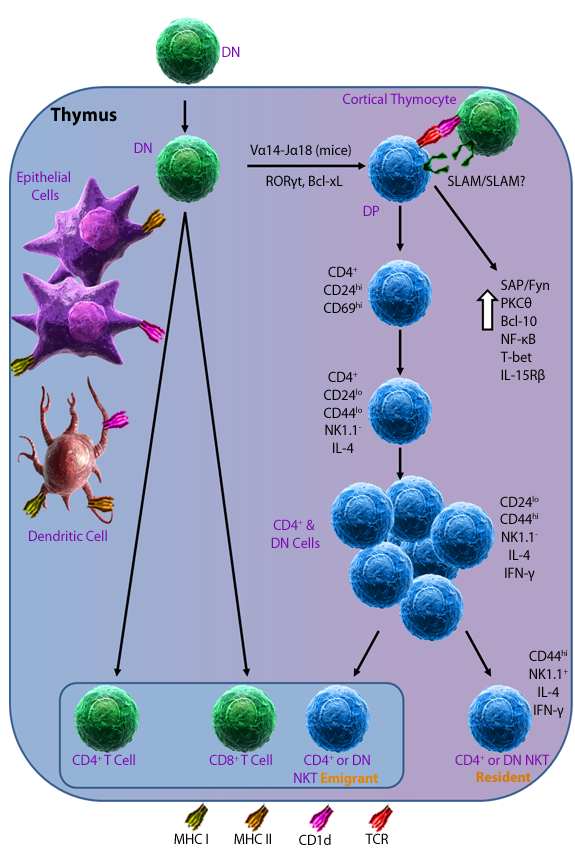 |
This adaptation from Bendelac, A. et al. 2007. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 25:336 represents mouse NKT cell development.
DN: Double Negative (CD4-, CD8-) T Cell; DP: Double Positive (CD4+, CD8+) T Cell
 Login / Register
Login / Register 






Follow Us