|

|
Embryonic Stem Cells
CD9, CD24, CD29, CD49f, CD117, CD133, CD324, SSEA-1, SSEA-3, SSEA-4, Tra-1-60, Tra-1-81
|

|
Ectoderm
CD15, CD29, CD49f, CD133, GFAP, Nestin, Neurofilament, Olig2, Pax6, SOX2
|
|

|
Endoderm CXCR4, FOXA2, GATA4, GATA6, SOX17
|

|
Mesoderm
CD10, CD16/32, CD34, CD38, CD45RA, CD48, CD90, CD117, CD123, CD127, CD133, CD135, CD150, Sca-1
|
 |
Hemangioblasts
Human: CD133
Mouse: Brachyury, CD135
Multipotent Progenitor
Human: CD34, CD90, CD135, Lin-
Mouse: CD34-, CD48-, CD117, CD150, Sca-1
Common Lymphoid Progenitor
(Differentiates into B cells, T cells, and ILC)
Human: CD10, CD34, CD45RA, CD135, Lin-
Mouse: CD117low, CD127, CD135, Lin-
Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitor
(Differentiates into Monocytes, Macrophages, Dendritic Cells, and Granulocytes)
Human: CD34, CD38, CD115, CD116, CD123
Mouse: CD16/32, CD34, CD117, Sca-1
|
Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Human: CD34, CD90, CD135, Lin-
Mouse: CD34-, CD48-, CD117, CD150, Sca-1
Common Myeloid Progenitor
Human: CD34, CD38, CD45RA-, CD135
Mouse: CD34, CD117, CD135, Sca-1-
Megakaryocyte-Erythrocyte Progenitor
(Differentiates into RBCs and Megakaryocytes)
Human: CD34, CD71, CD110
Mouse: CD34-, CD41, CD105, CD150
|
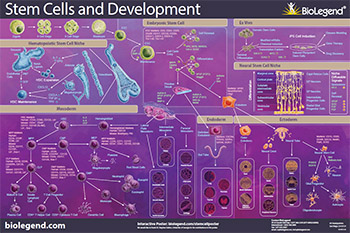 Stem cells are unique cells due to their capability to limitlessly self-renew and differentiate into each cell type in the adult body. Stem cells’ capability to differentiate depends on the stem cell type. Regardless of the type of stem cell you are working with, BioLegend offers stem cell-focused reagents for flow cytometry, cell screening, western blotting, ELISAs, cell differentiation, and more.
Stem cells are unique cells due to their capability to limitlessly self-renew and differentiate into each cell type in the adult body. Stem cells’ capability to differentiate depends on the stem cell type. Regardless of the type of stem cell you are working with, BioLegend offers stem cell-focused reagents for flow cytometry, cell screening, western blotting, ELISAs, cell differentiation, and more. Login / Register
Login / Register 











Follow Us