Ab initio.
From the beginning.
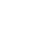
B cells are a lineage of lymphocytes originally discovered in the Bursa of Fabricus in birds (hence the B in B cells). B cell development in mammals was mainly found to occur in the bone marrow, as they do not have a Bursa of Fabricus. B cells are not only responsible for antibody production, but are also involved in several other areas of immunology. Click through the different sections of the shield to gain an understanding of everything B cells do in a mammalian system.
Want help designing your B Cell panel? Click here!
 Login/Register
Login/Register 








Follow Us