| Chemokines are a class of cytokines that induce chemotaxis (migration) of target cells. Chemokines work through concentration gradients. Attracted cells move toward areas of higher concentrations of the chemokine. While some chemotaxis is induced by inflammation or damaged cells, other chemokines function in homeostasis. | Chemokines receptors are seven transmembrane spanning G protein-coupled receptors that allow cells to migrate towards increasing chemokine gradients. The receptor N-terminus is external and contributes to ligand binding while the carboxy terminus (COOH) allows for interaction with signaling molecules and downstream signaling. |
Loading...

| X |
| Homeostasis: |
| Homeostatic chemokines are constitutively expressed in particular organs or tissues. Specific chemokine receptors are often required to gain entry (or exit) from certain organs and tissues like the thymus and bone marrow. These chemokines also have a more diverse range of functions compared to inflammatory chemokines. These functions include organogenesis, stem cell migration, and cell development. Due to their function of targeting cells to specific organs, homeostatic chemokines can also be involved in cancer and metastasis. For more information on homeostatic chemokines, see the review below: Zlotnik, A. et al. 2011. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11:597. Pubmed |
| X |
| Inflammation: |
| In the event of infection, injury, or tissue damage, inflammatory chemokines are often released to address the problem. Many inflammatory chemokines attract a wide variety of cells in both the innate and adaptive arms of immunity. Upon sensing the inflammatory chemokine, cells will extravasate from the blood vessel and follow the gradient to its source. Once at the site of injury, immune cells can react by releasing additional cytokines and chemokines, bringing more cells into the fold. Chemokines are also involved in the orchestration of wound healing. For more information on inflammatory chemokines, see the review below: Moser, B. and Willimann, K. 2004. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 63:84. Pubmed |
| Chemokine Structure and Classification | |
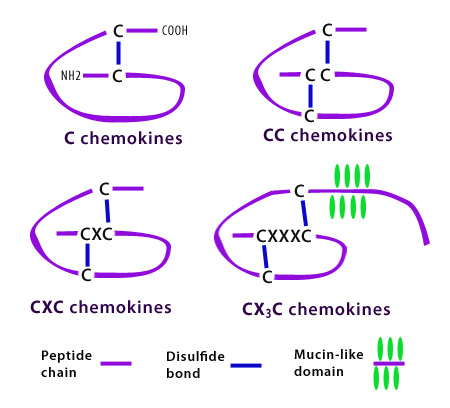 |
|
Chemokine Receptor Structure
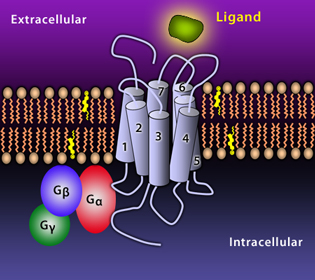
- Seven transmembrane regions
- Amino terminus (NH2) and extracellular loops contribute to the ligand specificity.
- G-coupled proteins at the carboxy terminus (COOH) allow for downstream signaling.
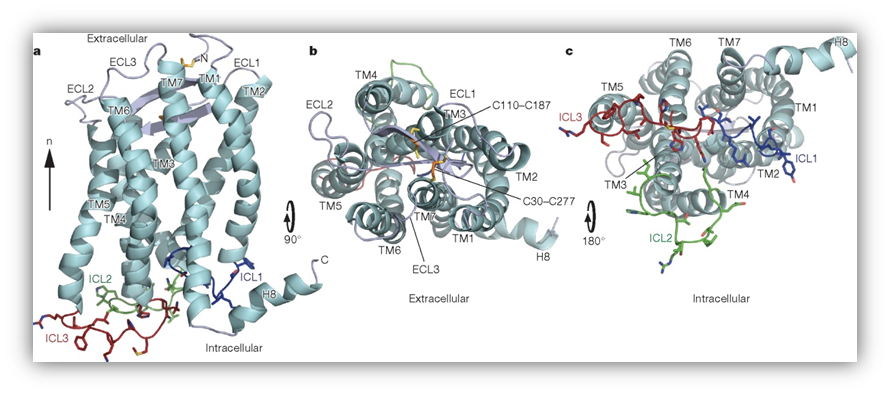
SH Park et al. Nature 491, 779 (2012) doi:10.1038/nature11580
Three-dimensional structure of CXCR1.
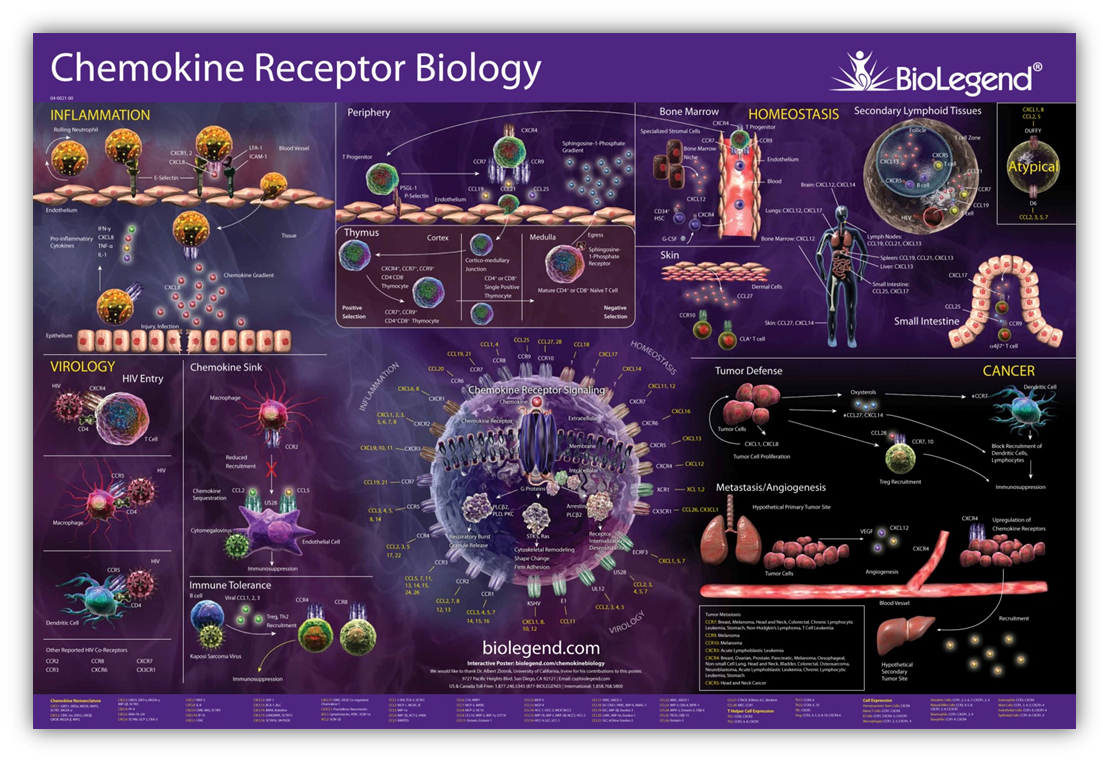
| Chemokine Receptor Biology poster |
| Order your copy of our poster here. Click on the image below to view the interactive pathway. |
 |
| Receptor-Ligand Table |
| Use this table to quickly identify the chemokines that bind to each receptor. Click on the receptor to sort the ligands to the top. |
| Ligand | CXCR1 | CXCR2 | CXCR3 | CXCR4 | CXCR5 | CXCR6 | CXCR7 | CX3CR1 | XCR1 | CCR1 | CCR2 | CCR3 | CCR4 | CCR5 | CCR6 | CCR7 | CCR8 | CCR9 | CCR10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CXCL1 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CXCL2 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CXCL3 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CXCL5 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CXCL6 |  |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| CXCL7 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CXCL8 |  |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| CXCL9 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CXCL10 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CXCL11 |  |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| CXCL12 |  |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| CXCL13 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CXCL16 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CX3CL1 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| XCL1 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| XCL2 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL1 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL2 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL3 |  |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| CCL3L1 |  |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| CCL4 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL5 |  |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||
| CCL7 |  |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||
| CCL8 |  |
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||
| CCL11 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL13 |  |
 |
 |
||||||||||||||||
| CCL14 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL15 |  |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| CCL16 |  |
 |
|||||||||||||||||
| CCL17 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL19 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL20 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL21 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL22 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL23 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL24 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL25 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL26 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL27 |  |
||||||||||||||||||
| CCL28 |  |
ProductsHere
 Login/Register
Login/Register 






Follow Us