- Clone
- GB11 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Granzyme-2, serine protease B, CCP1, Asp-ase, CTLA-1
- Isotype
- Mouse IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
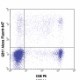
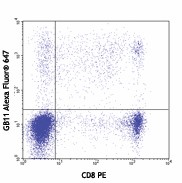
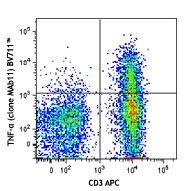
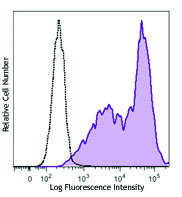
Human peripheral blood lymphocytes were surface stained with CD8 PE, then intracellularly stained with Granzyme B (clone GB11) Alexa Fluor® 647 (top) or mouse IgG1 Alexa Fluor® 647 isotype control (middle). -
-
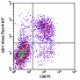
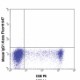
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stimulated with plate-bound anti-mouse TCR-β for 2 days, then surface stained with CD8 PE and intracellularly stained with Granzyme B (clone GB11) Alexa Fluor® 647.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 515405 | 25 tests | £117 | ||||
| 515406 | 100 tests | £249 | ||||
Granzyme B is a 32 kD serine protease, also known as granzyme-2, serine protease B, CCP1, Asp-ase, and CTLA-1. Granzyme B is abundantly stored in the granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and NK cells. Low level of expression has been reported in granulocytes, B cells, and activated dendritic cells. Granzyme B is crucial for rapid induction of cell death and apoptosis through interaction with mannose-6-phosphate receptor.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Reactivity
- Human,Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and BSA (origin USA)
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography and conjugated with Alexa Fluor® 647 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- Lot-specific (to obtain lot-specific concentration and expiration, please enter the lot number in our Certificate of Analysis online tool.)
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
ICFC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by intracellular immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µl per million cells in 100 µl staining volume or 5 µl per 100 µl of whole blood.
* Alexa Fluor® 647 has a maximum emission of 668 nm when it is excited at 633nm / 635nm.
Alexa Fluor® and Pacific Blue™ are trademarks of Life Technologies Corporation.
View full statement regarding label licenses - Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Wever PC, et al. 1998. Immunology. 93:383
- Arens R, et al. 2004. J. Exp. Med. 199:1595
- Lima M, et al. 2003. Am. J. Pathol. 163:763
- Wiede F, et al. 2014. J Autoimmun. 53:105. PubMed
- Baker GF, et al. 2014. Cancer Res. 74:5079. PubMed
- Nacer A, et al. 2014. PLoS Pathog. 10:1004528. PubMed
- Sharma SK, et al. 2015. J Immunol. 194:5529. PubMed
- Product Citations
- RRID
-
AB_2294995 (BioLegend Cat. No. 515405)
AB_2566333 (BioLegend Cat. No. 515406)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- 32 kD serine protease
- Distribution
-
Cytotoxic T-cells and NK cells, low on granulocytes, B cells and activated dendritic cells
- Function
- Induction of cell death and apoptosis
- Ligand/Receptor
- Mannose-6-phosphate receptor
- Cell Type
- B cells, Dendritic cells, NK cells, T cells
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Innate Immunity, Neuroscience
- Molecular Family
- Enzymes and Regulators, Proteases
- Antigen References
-
1. Estebanez-Perpina E, et al. 2000. Biol Chem. 381:1203
2. Griffiths GM. And S. Isaaz, et al. 1993. J. Cell Biol. 120:885
3. Spaeny-Dekking EH, et al. 1998. J. Immunol. 160:3610
4. Wagner C, et al. 2008. Mol. Immunol. 45:1761 - Gene ID
- 3002 View all products for this Gene ID 14939 View all products for this Gene ID 171528 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about Granzyme B on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
Customers Also Purchased
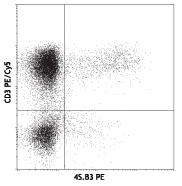
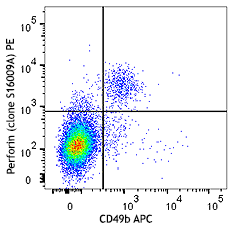
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 












Follow Us