- Clone
- M1/70 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- αM integrin, Mac-1, Mo1, CR3, Ly-40, C3biR, ITGAM
- Isotype
- Rat IgG2b, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
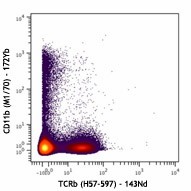
-

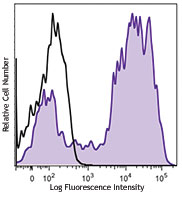
Mouse splenocytes stained with 172Yb-anti-CD11b (M1/70) and 143Nd-anti-TCRb (H57-597). Data provided by DVS Sciences.
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101249 | 100 µg | 85€ | ||||
CD11b is a 170 kD glycoprotein also known as αM integrin, Mac-1 α subunit, Mol, CR3, and Ly-40. CD11b is a member of the integrin family, primarily expressed on granulocytes, monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells, NK cells, and subsets of T and B cells. CD11b non-covalently associates with CD18 (β2 integrin) to form Mac-1. Mac-1 plays an important role in cell-cell interaction by binding its ligands ICAM-1 (CD54), ICAM-2 (CD102), ICAM-4 (CD242), iC3b, and fibrinogen.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Reactivity
- Mouse,Human,Cynomolgus,Rhesus
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- C57BL/10 splenocytes
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and EDTA.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 1.0 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
CyTOF® - Verified - Recommended Usage
-
This product is suitable for use with the Maxpar® Metal Labeling Kits. For metal labeling using Maxpar® Ready antibodies, proceed directly to the step to Partially Reduce the Antibody by adding 100 µl of Maxpar® Ready antibody to 100 µl of 4 mM TCEP-R in a 50 kDa filter and continue with the protocol. Always refer to the latest version of Maxpar® User Guide when conjugating Maxpar® Ready antibodies.
- Application Notes
-
Clone M1/70 has been verified for immunocytochemistry (ICC) and frozen immunohistochemistry (IHC-F).
Additional reported applications (for relevant formats of this clone) include: immunoprecipitation1,4, in vitro blocking3,9,12, depletion2,8, immunofluorescence microscopy6,7,10, immunohistochemistry of acetone-fixed frozen sections5,11-13, and spatial biology (IBEX)35,36. For in vivo studies or highly sensitive assays, we recommend Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin < 0.01 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) (Cat. No. 101248). - Additional Product Notes
-
Maxpar® is a registered trademark of Standard BioTools Inc.
- Application References
-
- Springer T, et al. 1978. Eur. J. Immunol. 8:539. (IP)
- Ault K and Springer T. 1981. J. Immunol. 126:359. (Deplete)
- Springer TA, et al. 1982. Immunol. Rev. 68:171. (Block)
- Ho MK and Springer TA. 1983. J. Biol. Chem. 258:2766. (IP)
- Flotte TJ, et al. 1983. Am. J. Pathol. 111:112. (IHC)
- Noel GJ, et al. 1990. J. Clin. Invest. 85:208. (IF)
- Allen LA and Aderem A. 1996. J. Exp. Med. 184:627 (IF)
- D'Amico A and Wu L. 2003. J. Exp. Med. 198:293. (Deplete)
- Brickson SJ, et al. 2003. Appl Physiol. 95:969. (Block)
- Clatworthy MR and Smith KG. 2004. J. Exp. Med. 199:717. (IF)
- Hata H, et al. 2004. J. Clin. Invest. 114:582. (IHC)
- Zhang Y, et al. 2002. J. Immunol. 168:3088. (IHC)
- Iwasaki A and Kelsall BL. 2001. J. Immunol. 166:4884 (IHC, FC)
- Tailleux L. 2003. J. Exp. Med. 197:121. (Block, FC)
- Olver S, et al. 2006. Cancer Research 66:571. (FC)
- Tan SL, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 176:2872. (FC) PubMed
- Ponomarev ED, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 176:1402. (FC)
- Dzhagalov I, et al. 2007. Blood 109:1620. (FC)
- Fazilleau N, et al. 2007. Nature Immunol. 8:753.
- Rasmussen JW, et al. 2006. Infect. Immun.74:6590. PubMed
- Napimoga MH, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 180:609. PubMed
- Elqaraz-Carmon V, et al. 2008. J. Lipid. Res. 49:1894. PubMed
- Kim DD, et al. 2008. Blood 112:1109. PubMed
- Guo Y, et al. 2008. Blood 112:480. PubMed
- Norian LA, et al. 2009. Cancer Res. 69:3086. (FC) PubMed
- Baumgartner CK, et al. 2010. J. Immunol. 184:573. PubMed
- Charles N, et al. 2010. Nat. Med. 16:701. (FC) PubMed
- Whiteland J, et al. 1995. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 43:313. (IHC)
- Weber GF, et al. 2014. J Exp Med. 211:1243. PubMed
- Ashok A, et al. 2015. Toxicol Sci. 143:64. PubMed
- Price PJ, et al. 2015. J Immunol. 194:1164. PubMed
- Doni A, et al. 2015. J Exp Med. 212:905. PubMed
- Ferreira R, et al. 2016. J Infect Dis. 213: 669 - 673. PubMed
- Peterson VM, et al. 2017. Nat. Biotechnol. 35:936. (PG)
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2020. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 117:33455-65. (SB) PubMed
- Radtke AJ, et al. 2022. Nat Protoc. 17:378-401. (SB) PubMed
- Product Citations
- RRID
-
AB_2562797 (BioLegend Cat. No. 101249)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Integrin family, associates with integrin β2 (CD18), 170 kD
- Distribution
-
Granulocytes, monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells, NK cells, subsets of T and B cells
- Function
- Adhesion, chemotaxis
- Ligand/Receptor
- ICAM-1 (CD54), ICAM-2 (CD102), ICAM-4 (CD242), iC3b, fibrinogen
- Cell Type
- B cells, Dendritic cells, Granulocytes, Macrophages, Monocytes, Neutrophils, NK cells, T cells, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Cell Adhesion, Cell Biology, Costimulatory Molecules, Immunology, Innate Immunity, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- Adhesion Molecules, CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay A, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Springer TA. 1994. Cell 76:301.
3. Coxon A, et al. 1996. Immunity 5:653. - Gene ID
- 16409 View all products for this Gene ID 3684 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD11b on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- Can I obtain CyTOF data related to your Maxpar® Ready antibody clones?
-
We do not test our antibodies by mass cytometry or on a CyTOF machine in-house. The data displayed on our website is provided by Fluidigm®. Please contact Fluidigm® directly for additional data and further details.
- Can I use Maxpar® Ready format clones for flow cytometry staining?
-
We have not tested the Maxpar® Ready antibodies formulated in solution containing EDTA for flow cytometry staining. While it is likely that this will work in majority of the situations, it is best to use the non-EDTA formulated version of the same clone for flow cytometry testing. The presence of EDTA in some situations might negatively affect staining.
- I am having difficulty observing a signal after conjugating a metal tag to your Maxpar® antibody. Please help troubleshoot.
-
We only supply the antibody and not test that in house. Please contact Fluidigm® directly for troubleshooting advice: http://techsupport.fluidigm.com/
- Is there a difference between buffer formulations related to Maxpar® Ready and purified format antibodies?
-
The Maxpar® Ready format antibody clones are formulated in Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide and EDTA. The regular purified format clones are formulated in solution that does not contain any EDTA. Both formulations are however without any extra carrier proteins.
Customers Also Purchased
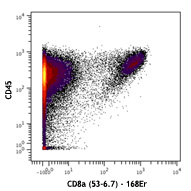
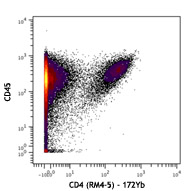
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 












Follow Us