- Clone
- 104 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Ly-5.2, LCA
- Isotype
- Mouse (SJL) IgG2a, κ
-
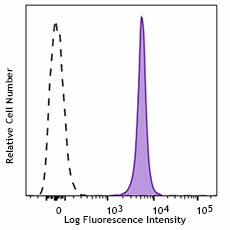
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 104) APC/Cyanine7 (filled histogram) or Mouse IgG2a, ? APC/Cyanine7 isotype control (open histogram).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 109823 | 25 µg | $116.00 | |||
| 109824 | 100 µg | $292.00 | |||
CD45.2 is an alloantigen of CD45, expressed by Ly5.2 bearing mouse strains (e.g., A, AKR, BALB/c, CBA/Ca, CBA/J, C3H/He, C57BL, C57BR, C57L, C58, DBA/1, DBA/2, NZB, SWR, 129). CD45, a member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family, is a 180-240 kD glycoprotein expressed on all hematopoietic cells except mature erythrocytes and platelets. There are multiple isoforms in the mouse that play key roles in TCR and BCR signal transduction. These isoforms are very specific to the activation and maturation states of the cell as well as specific cell type. The primary ligands for CD45 are galectin-1, CD2, CD3, CD4, TCR, CD22, and Thy-1.
Product Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Immunogen
- B10.S mouse thymocytes and splenocytes
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with APC/Cyanine7 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is =1.0 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Red Laser (633 nm)
- Application Notes
-
The 104 antibody does not react with mouse cells expressing the CD45.1 alloantigen. Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation4, in vivo and in vitro blocking of B cell responses1,2, and immunohistochemical staining of acetone-fixed frozen sections3.
- Additional Product Notes
- BioLegend is in the process of converting the name APC/Cy7 to APC/Cyanine7. The dye molecule remains the same, so you should expect the same quality and performance from our APC/Cyanine7 products. Please contact Technical Service if you have any questions.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Yakura H, et al. 1983. J. Exp. Med. 157:1077. (Block)
- Yakura H, et al. 1986. J. Immunol. 136:2729. (Block)
- Suzuki K, et al. 2000. Immunity 13:691. (IHC)
- Shen FW, et al. 1986. Immunogenetics 24:146. (IP)
- Baldwin TA and Hogquist KA. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:837.
- Pascal V, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:1751.
- Burman AC, et al. 2007. Blood 110:1064.
- Kincaid EZ, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:3187.
- Phan TG, et al. 2007. Nature Immunol. 8:992.
- Nakano-Yokomizo T, et al. 2011. J. Exp Med. 208:1661. PubMed
- Wen T, et al. 2013. PNAS. 110:6067. PubMed
- Kohlmeier JE, et al. 2008. Immunity. 29:101. (FC) PubMed
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_830788 (BioLegend Cat. No. 109823)
AB_830789 (BioLegend Cat. No. 109824)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family, 180-240 kD
- Distribution
-
All hematopoietic cells except mature erythrocytes and platelets of the CD45.2 strain of mice
- Function
- Phosphatase, T and B cell activation
- Ligand/Receptor
- Galectin-1, CD2, CD3, CD4
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Inhibitory Molecules, Innate Immunity, Neuroscience, Neuroscience Cell Markers
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules
- Antigen References
-
1. Suzuki K, et al. 2000. Immunity 13:691.
- Gene ID
- 19264 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD45.2 on UniProt.org
Other Formats
View All CD45.2 Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCompare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
Biotin anti-mouse CD45.2
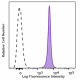
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with biotinylated 104, fol... -
FITC anti-mouse CD45.2
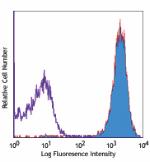
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 104 FITC -
PE anti-mouse CD45.2
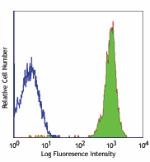
BALB/c (solid line) and SJL (broken line) splenocytes staine... -
Purified anti-mouse CD45.2
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with purified 104, followe... -
APC anti-mouse CD45.2
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 104 APC -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD45.2
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 104 Alexa Fluor® 488 -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD45.2
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 104 Alexa Fluor® 647 -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD45.2
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with Pacific Blue™ 1... -
Alexa Fluor® 700 anti-mouse CD45.2
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 104 Alexa Fluor® ... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD45.2
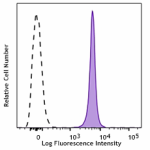
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
PerCP anti-mouse CD45.2
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 104 PerCP -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD45.2
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 104 PerCP/Cyanine5.5 -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD45.2
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes stained with 104 PE/Cyanine7 -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD45.2
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
Brilliant Violet 570™ anti-mouse CD45.2
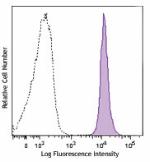
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
Brilliant Violet 650™ anti-mouse CD45.2
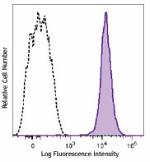
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse CD45.2
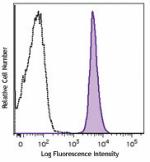
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD45.2
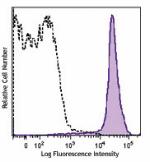
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD45.2
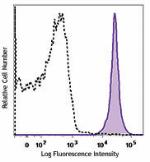
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
Purified anti-mouse CD45.2 (Maxpar® Ready)
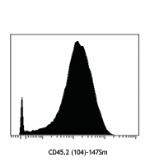
C57BL/6 mouse bone marrow cells stained with 147Sm-anti-CD45... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD45.2
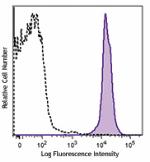
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse CD45.2
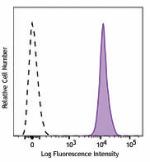
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
Alexa Fluor® 594 anti-mouse CD45.2
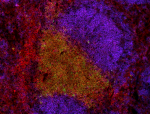
BALB/C mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafor... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD45.2
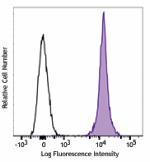
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
TotalSeq™-A0157 anti-mouse CD45.2
-
TotalSeq™-B0157 anti-mouse CD45.2
-
TotalSeq™-C0157 anti-mouse CD45.2
-
Brilliant Violet 750™ anti-mouse CD45.2
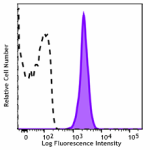
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
Spark Blue™ 550 anti-mouse CD45.2
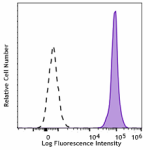
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD45.2 (clone 10... -
Spark NIR™ 685 anti-mouse CD45.2
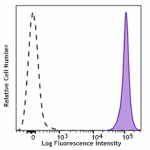
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD45.... -
Spark UV™ 387 anti-mouse CD45.2
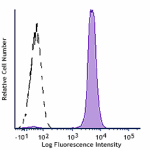
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD45.... -
Spark Blue™ 574 anti-mouse CD45.2 (Flexi-Fluor™)
-
Spark Red™ 718 anti-mouse CD45.2 (Flexi-Fluor™)
