- Clone
- TC11-18H10.1 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Interleukin-17, Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 8 (CTLA-8)
- Isotype
- Rat IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 506901 | 50 µg | $106 | ||||
| 506902 | 500 µg | $282 | ||||
IL-17, also known as CTLA-8, is a T cell-expressed pleiotropic cytokine that exhibits a high degree of homology to a protein encoded by the ORF13 gene of herpes virus Saimiri. IL-17 is produced by Th cells (Th17) that are distinct from the traditional Th1- and Th2-cell subsets. IL-23 plays an important role in triggering IL-17 production. Both recombinant and natural IL-17 have been shown to exist as disulfide linked homodimers. IL-17 exhibits multiple biological activities on a variety of cells including: the induction of IL-6 and IL-8 production in fibroblasts, activation of NF-κB, and costimulation of T cell proliferation. IL-17 is an essential inflammatory mediator in the development of autoimmune diseases. Neutralization of IL-17 with monoclonal antibody is able to ameliorate the disease course.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- E. coli expressed, recombinant mouse IL-17A
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
ELISA Capture - Quality tested
CyTOF® - Verified
ELISPOT Capture, ICFC - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
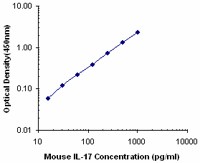
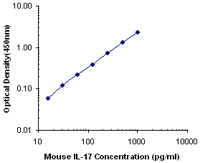
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by ELISA assay. For ELISA capture, a concentration range of 1-4 µg/ml is recommended. To obtain a linear standard curve, serial dilutions of IL-17 recombinant protein ranging from 1000 to 15.63 pg/mL are recommended for each ELISA plate. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
ELISA Capture3,4 and ELISPOT Capture5: The purified TC11-18H10.1 antibody is useful as the capture antibody in a sandwich ELISA, when used in conjunction with the biotinylated TC11-8H4 antibody (Cat. No. 507002) as the detecting antibody and recombinant mouse IL-17 (Cat. No. 576009) as the standard.
Flow Cytometry2-4,7,8,11,12: The TC11-18H10.1 antibody is useful for intracellular immunofluorescent staining and flow cytometric analysis to identify IL-17-producing cells within mixed cell populations.
Neutralization6,9: The LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin <0.1 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for neutralization of mouse IL-17 bioactivity in vivo and in vitro (Cat. No. 506906). -
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Kennedy J, et al. 1996. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 16:611.
- Schubert D, et al. 2004. J. Immunol. 172:4503. (ICFC)
- Infante-Duarte C, et al. 2000. J. Immunol. 165:6107. (ICFC, ELISA Capture)
- Harrington LE, et al. 2005. Nature Immunol. doi:10.1038/ni1254. (ICFC, ELISA Capture)
- Nekrasova T, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 175:2734. (ELISPOT Capture)
- Yen D, et al. 2006. J. Clin. Invest. 116:1310. (Neut)
- Ehirchiou D, et al. 2007. J. Exp. Med. 204:1519. (ICFC)
- Kang SG, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:3724. (ICFC)
- Smith E, et al. 2008. J. Immunol. 181:1357. (Neut) PubMed
- Neufert C, et al. 2007. Eur. J. Immunol. 37:1809. PubMed
- Wang C, et al. 2009. Mucosal Immunol 2:173. (ICFC) PubMed
- Cui Y, et al. 2009. Invest. Ophth. Vis. Sci. 50:5811. (ICFC) PubMed
- Kivisäkk P, et al. 2009. Ann. Neurol. 65:457. PubMed
- Cooney LA, et al. 2011. J. Immunol. 187:4440. PubMed
- Ma Y, et al. 2012. PLoS One. 7:e40763. PubMed
- Murakami R, et al. 2013. PLoS One. 8:73270. PubMed
- Product Citations
- RRID
-
AB_315461 (BioLegend Cat. No. 506901)
AB_315462 (BioLegend Cat. No. 506902)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Cytokine; dimer; 15 kD (Mammalian).
- Bioactivity
- Secretion of IL-6, IL-8, G-CSF, prostaglandin E2 by epithelial, endothelial or fibroblastic cells; stimulates cell migration, cord formation, and IL-6 secretion by stromal cells
- Cell Sources
- CD4+ memory T cells
- Cell Targets
- Fibroblasts, epithelial and endothelial cells, stromal cells
- Receptors
- IL-17R (CD217)
- Biology Area
- Cell Biology, Immunology, Neuroinflammation, Neuroscience
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Fitzgerald K, et al. Eds. 2001. The Cytokine FactsBook. Academic Press San Diego.
2. Numasaki M, et al. 2002. Blood 101:2620.
3. Fossiez F, et al. 1996. J. Exp. Med. 183:2593.
4. Yao Z, et al. 1997. Cytokine 9:794.
5. Dong C. 2006. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6:329.
6. Hofstetter HH, et al. 2005 Cell. Immunol. 237:123. - Gene ID
- 16171 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about IL-17A on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- Does the anti-mouse IL-17 antibody (clone TC11-18H10.1) recognize the A or F isoform?
- Clone TC11-18H10.1 recognizes IL-17A isoform, but it also recognizes the IL-17A/F heterodimer via IL-17A binding.
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
 Login/Register
Login/Register 








Follow Us