- Clone
- 145-2C11 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- CD3ε, T3, CD3
- Isotype
- Armenian Hamster IgG
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
-
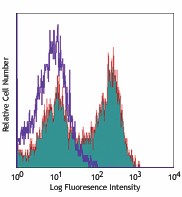
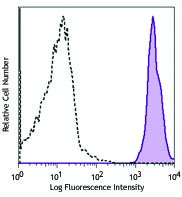
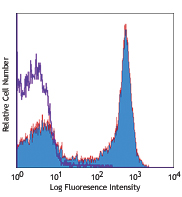
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-2C11) PE/Cyanine7 (filled histogram) or Armenian hamster IgG PE/Cyanine7 isotype control (open histogram).
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100319 | 25 µg | 88 CHF | ||||
| 100320 | 100 µg | 198 CHF | ||||
CD3ε is a 20 kD transmembrane protein, also known as CD3 or T3. It is a member of the Ig superfamily and primarily expressed on T cells, NK-T cells, and at different levels on thymocytes during T cell differentiation. CD3ε forms a TCR complex by associating with the CD3δ, γ and ζ chains, as well as the TCR α/β or γ/δ chains. CD3 plays a critical role in TCR signal transduction, T cell activation, and antigen recognition by binding the peptide/MHC antigen complex.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Verified Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Armenian Hamster
- Immunogen
- H-2Kb-specific mouse cytotoxic T lymphocyte clone BM10-37
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE/Cyanine7 under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.5 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
Clone 145-2C11 is useful for in vitro blocking of target-specific CTL-mediated cell lysis1, as well as T cell activation assays, inducing proliferation and cytokine production1,2,7,12,16. It also induces apoptosis in immature thymocytes32, and in vivo T cell depletion8-10. Additional reported applications (for relevant formats of this clone) include: immunoprecipitation1, immunohistochemical staining14,15 of acetone-fixed frozen sections and zinc-fixed paraffin-embedded sections, Western blotting4, complement-mediated cytotoxicity6, in vitro and in vivo stimulation of T cells1,2,7,12,16, immunofluorescent staining5, and in vivo T cell depletion8-10. The 145-2C11 antibody has been reported to block the binding of 17A2 antibody to CD3 epsilon-specific T cells11. Clone 145-2C11 is not recommended for formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sections. The LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin <0.1 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for functional assays (Cat. No. 100314). For in vivo studies or highly sensitive assays, we recommend Ultra-LEAF™ purified antibody (Cat. No. 100340) with a lower endotoxin limit than standard LEAF™ purified antibodies (Endotoxin <0.01 EU/µg).
- Additional Product Notes
- BioLegend is in the process of converting the name PE/Cy7 to PE/Cyanine7. The dye molecule remains the same, so you should expect the same quality and performance from our PE/Cyanine7 products. Please contact Technical Service if you have any questions.
-
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Leo O, et al. 1987. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:1374. (IP, Activ, Block)
- Kruisbeek AM, et al. 1991. In Current Protocols in Immunology. 3.12.1. (Activ)
- Duke RC, et al. 1995. Current Protocols in Immunology. 3.17.1.
- Salvadori S, et al. 1994. J. Immunol. 153:5176. (WB)
- Payer E, et al. 1991. J. Immunol. 146:2536. (IF)
- Jacobs H, et al. 1994. Eur. J. Immunol. 24:934. (CMCD)
- Vossen ACTM, et al. 1995. Eur. J. Immunol. 25:1492. (Activ)
- Henrickson M, et al. 1995. Transplantation 60:828. (Deplete)
- Kinnaert P, et al. 1996. Transpl. Int. 9:386. (Deplete)
- Han WR, et al. 1999. Transpl. Immunol. 7:207. (Deplete)
- Miescher GC, et al. 1989. Immunol. Lett. 23:113. (Block)
- Terrazas LI, et al. 2005. Intl. J. Parasitology. 35:1349. (Activ)
- Ko SY, et al. 2005. J. Immunol. 175:3309.
- Podd BS, et al. 2006. J. Immunol. 176:6532. (IHC-F)
- Tilley SL, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:3208. (IHC-F)
- Wang W, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:4885. (Activ)
- Xiao S, et al. 2007. J. Exp. Med. 204:1691.
- Chappaz S, et al. 2007. Blood doi:10.1182/blood-2007-02-074245. (FC) PubMed.
- Curtsinger JM, et al.2005. J. Immunol. 175:4392. PubMed
- Guo Y, et al. 2008. Blood 112:480. PubMed
- Kenna TJ, et al. 2008. Blood 111:2091.
- Perchonock CE, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:1768. PubMed
- Perchonock GE, et al. 2006. Mol. Cell. Biol. 26:6005. PubMed
- Kanaya T, et al. 2008. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 295:G273. PubMed
- de Koning BA, et al. 2006. Int. Immunol. 18:941. PubMed
- Schulteis RD, et al. 2008. Blood 295:G273. PubMed
- Qi Q, et al. 2009. Blood 114:564. PubMed
- Helmersson S, et al. 2013. Am J Pathol. 9440:123. Pubmed
- Wu S, et al. 2014. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 21:156. PubMed
- Yan J, et al. 2014. Vaccine. 32:2833. PubMed
- Guiterrez DA, et al. 2014. Diaebetes. 63:3827. PubMed
- Shi YF, et al. 1991. J Immunol. 146:3340. (Apop)
- Product Citations
-
- RRID
-
AB_312684 (BioLegend Cat. No. 100319)
AB_312685 (BioLegend Cat. No. 100320)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Ig superfamily, forms CD3/TCR complex with CD3δ, γ and ζ subunits and TCR (α/β and γ/δ), 20 kD
- Distribution
-
Thymocytes (differentiation dependent), mature T cells, NK-T cells
- Function
- TCR signal transduction, T cell activation, antigen recognition
- Ligand/Receptor
- Peptide antigen/MHC-complex
- Cell Type
- NKT cells, T cells, Thymocytes, Tregs
- Biology Area
- Immunology
- Molecular Family
- CD Molecules, TCRs
- Antigen References
-
1. Barclay A, et al. 1997. The Leukocyte Antigen FactsBook Academic Press.
2. Davis MM. 1990. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 59:475.
3. Weiss A, et al. 1994. Cell 76:263. - Gene ID
- 12501 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about CD3epsilon on UniProt.org
Related Pages & Pathways
Pages
Other Formats
View All CD3ε Reagents Request Custom ConjugationCustomers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
-
APC anti-mouse CD3ε
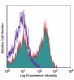
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... -
Biotin anti-mouse CD3ε
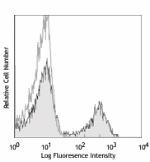
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with biotinylated CD3... 
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... -
FITC anti-mouse CD3ε

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... -
PE anti-mouse CD3ε

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... 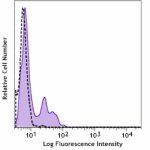
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... -
PE/Cyanine5 anti-mouse CD3ε
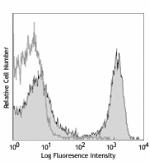
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... -
Purified anti-mouse CD3ε
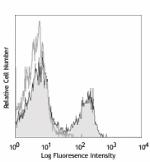
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with purified CD3e (c... 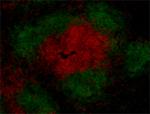
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 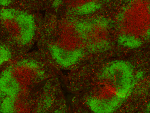
Fresh, frozen mouse spleen was stained with purified CD3ε cl... -
PE/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD3ε
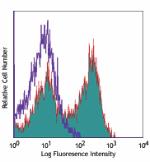
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... -
Alexa Fluor® 488 anti-mouse CD3ε
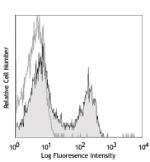
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... -
Alexa Fluor® 647 anti-mouse CD3ε
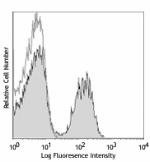
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... 
C57BL/6 mouse frozen spleen section was fixed with 4% parafo... 
Paraformaldehyde-fixed (4%), 500 μm-thick mouse spleen secti... -
PerCP anti-mouse CD3ε
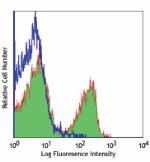
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... -
PerCP/Cyanine5.5 anti-mouse CD3ε
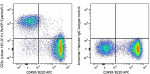
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD45R/B220 APC and CD3... -
Purified anti-mouse CD3ε (Maxpar® Ready)
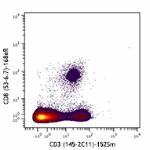
Mouse splenocytes stained with 152Sm anti-CD3e (145-2C11) an... -
APC/Cyanine7 anti-mouse CD3ε
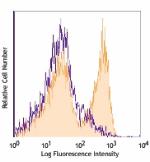
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... -
Pacific Blue™ anti-mouse CD3ε
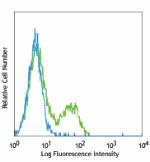
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3e (clone 145-... -
Brilliant Violet 421™ anti-mouse CD3ε

C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD19 FITC and CD... 
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyd... 
-
Ultra-LEAF™ Purified anti-mouse CD3ε
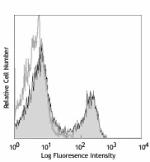
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with LEAF™ purified C... -
PE/Dazzle™ 594 anti-mouse CD3ε
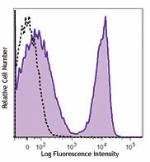
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3ε (cl... -
Brilliant Violet 510™ anti-mouse CD3ε
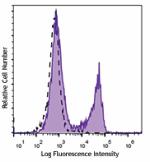
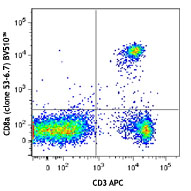
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3ε (cl... -
Brilliant Violet 605™ anti-mouse CD3ε
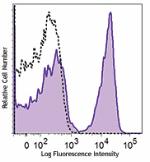
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3ε (cl... -
Brilliant Violet 711™ anti-mouse CD3ε
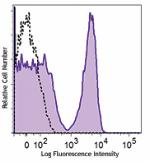
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3ε (cl... -
Brilliant Violet 785™ anti-mouse CD3ε
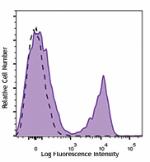
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with CD3ε (cl... -
APC/Fire™ 750 anti-mouse CD3ε
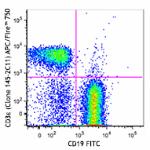
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with CD19 FITC and CD3&epsi... 
-
GoInVivo™ Purified anti-mouse CD3ε
-
Spark YG™ 593 anti-mouse CD3
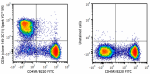
C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD45R/B220 ... -
PerCP/Fire™ 780 anti-mouse CD3ε
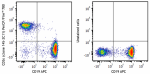
C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes were stained with anti-mouse CD19...
 Login / Register
Login / Register 













Follow Us