- Clone
- 11B11 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Other Names
- Interleukin-4, Ia inducing factor (IaIF), B cell stimulating factor-1 (BSF-1), Hodgkin's cell growth factor (HCGF), Mast cell growth factor-2 (MCGF-2), Macrophage fusion factor (MFF), T cell growth factor-2 (TCGF-2)
- Isotype
- Rat IgG1, κ
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 504101 | 50 µg | 83 CHF | ||||
| 504102 | 500 µg | 127 CHF | ||||
IL-4 is a pleiotropic cytokine produced by activated T cells, mast cells, and basophils. IL-4 is a potent lymphoid cell growth factor which stimulates the growth and activation of certain B cells and T cells. IL-4 is important for regulation of T helper subset development.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Monoclonal
- Host Species
- Rat
- Immunogen
- Partially purified native mouse IL-4
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide.
- Preparation
- The antibody was purified by affinity chromatography.
- Concentration
- 0.5 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C.
- Application
-
ELISA Capture - Quality tested
CyTOF® - Verified
IP, IHC, ICC - Reported in the literature, not verified in house - Recommended Usage
-
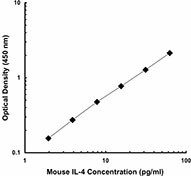
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by ELISA assay. For ELISA capture applications, a concentration range of 0.5-2.0 µg/ml is recommended. To obtain a linear standard curve, serial dilutions of IL-4 recombinant protein ranging from 250 to 2 pg/ml are recommended for each ELISA plate. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Application Notes
-
ELISA1,2,10,13 or ELISPOT5 Capture: The purified 11B11 antibody is useful as the capture antibody in a sandwich ELISA or ELISPOT assay, when used in conjunction with the biotinylated BVD6-24G2 antibody (Cat. No. 504202) as the detecting antibody and recombinant mouse IL-4 (Cat. No. 575609) as the standard. The LEAF™ purified antibody is suggested for ELISPOT capture.
Neutralization1-2,9,12: The 11B11 antibody can neutralize the bioactivity of natural or recombinant IL-4. The LEAF™ purified antibody (Endotoxin <0.1 EU/µg, Azide-Free, 0.2 µm filtered) is recommended for neutralization of mouse IL-4 bioactivity in vivo and in vitro (Cat. No. 504108).
Additional reported applications (for the relevant formats) include: immunoprecipitation16, immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections8 and paraformaldehyde-fixed, saponin-treated frozen tissue sections6,7, and immunocytochemistry4.
Note: For testing mouse IL-4 in serum, plasma or supernatant, BioLegend's ELISA Max™ Sets (Cat. No. 431101 to 431106) are specially developed and recommended. -
Application References
(PubMed link indicates BioLegend citation) -
- Shirai A, et al. 1994. Cytokine 6:329. (ELISA, Neut)
- Abrams J. 1995. Curr. Prot. Immunol. John Wiley and Sons New York. Unit 6.20. (ELISA, Neut)
- Assenmacher M, et al. 1994. Eur. J. Immunol. 24:1097.
- Openshaw P, et al. 1995. J. Exp. Med. 182:1357. (ICC)
- Klinman D, et al. 1994. Curr. Prot. Immunol. John Wiley and Sons New York. Unit 6.19. (ELISA Capture)
- Litton M, et al. 1994. J. Immunol. Methods 175:47. (IHC)
- Andersson U, et al. 1999. Detection and quantification of gene expression. New York:Springer-Verlag. (IHC)
- Fan WY, et al. 2001. Exp. Biol. Med. 226:1045. (IHC)
- Hara M, et al. 2001. J. Immunol. 166:3789. (Neut)
- Dzhagalov I, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:2113. (ELISA)
- Lawson BR, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:5366.
- Wang W, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 178:4885. (Neut)
- Xu G, et al. 2007. J. Immunol. 179:5358. (ELISA) PubMed
- Ohnmacht C, et al. 2008. Blood 113:2816. PubMed
- Charles N, et al. 2010. Nat. Med. 16:701. (FC) PubMed
- Zavorotinskaya T, et al. 2003. Mol. Ther. 7:155. (IP)
- Product Citations
- RRID
-
AB_315315 (BioLegend Cat. No. 504101)
AB_315316 (BioLegend Cat. No. 504102)
Antigen Details
- Structure
- Cytokine; 15-19 kD (Mammalian)
- Bioactivity
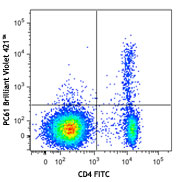
- Differentiation of naïve CD4+ T cells to the TH2 type, proliferation/differentiation of activated B cells, expression of class II MHC antigens, and of low affinity IgE receptors in resting B cells
- Cell Sources
- Mast cells, T cells, bone marrow stromal cells
- Cell Targets
- B cells, T cells, monocytes, endothelial cells, fibroblasts
- Receptors
- Heterodimer IL-4Rα (CD124); γ-subunit (CD132) in common with IL-2R, IL-7R, IL-13R, IL-15R
- Cell Type
- Tregs
- Biology Area
- Immunology
- Molecular Family
- Cytokines/Chemokines
- Antigen References
-
1. Fitzgerald K, et al. Eds. 2001. The Cytokine FactsBook. Academic Press San Diego.
2. Boulay J, et al. 1992. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 4:294.
3. Dullens H, et al. 1991. In vivo 5:567.
4. Paul W. 1991. Blood 77:1859. - Regulation
- Upregulated by IL-2, platelet activating factor; downregulated by TGF-β
- Gene ID
- 16189 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about IL-4 on UniProt.org
Customers Also Purchased
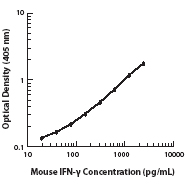
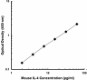
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 









Follow Us