- Clone
- Poly4053 (See other available formats)
- Regulatory Status
- RUO
- Isotype
- Goat Polyclonal IgG
- Ave. Rating
- Submit a Review
- Product Citations
- publications
| Cat # | Size | Price | Quantity Check Availability | Save | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 405307 | 200 µg | 176€ | ||||
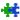
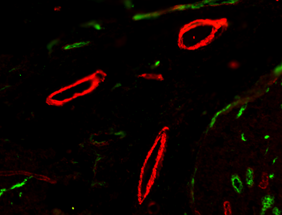
This polyclonal goat anti-mouse IgG antibody reacts with the heavy chains of mouse IgG and with the light (kappa and lambda) chains common to most mouse immunoglobulins. No cross-reactivity has been detected against non-immunoglobulin serum proteins. This antibody has been solid-phase absorbed to ensure minimal cross-reaction with rat, human, bovine, horse, and rabbit immunoglobulins, but it may have minimal cross-reactivity with other subclasses of mouse immunoglobulins.
Product DetailsProduct Details
- Reactivity
- Mouse
- Antibody Type
- Polyclonal
- Host Species
- Goat
- Formulation
- Phosphate-buffered solution, pH 7.2, containing 0.09% sodium azide
- Preparation
- The IgG antibody was purified by affinity chromatography, and conjugated with PE under optimal conditions.
- Concentration
- 0.2 mg/ml
- Storage & Handling
- The IgG antibody solution should be stored undiluted between 2°C and 8°C, and protected from prolonged exposure to light. Do not freeze.
- Application
-
FC - Quality tested
- Recommended Usage
-
Each lot of this antibody is quality control tested by immunofluorescent staining with flow cytometric analysis. For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is ≤0.5 µg per million cells in 100 µl volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application.
- Excitation Laser
-
Blue Laser (488 nm)
Green Laser (532 nm)/Yellow-Green Laser (561 nm)
- Application Notes
-
This polyclonal goat anti-mouse IgG antibody is useful for capture or detection of mouse IgG in ELISA.
- Application References
-
- Scotta C, et al. 2008. J Immunol. 181:1025-33. PubMed
- Gao X, et al. 2014. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 34:257-68 (ICC)
- Winters T, et al. 2014. EMBO J. 33:1256-70.
- Product Citations
- RRID
-
AB_315010 (BioLegend Cat. No. 405307)
Antigen Details
- Distribution
-
B cells
- Gene ID
- 16059 View all products for this Gene ID
- UniProt
- View information about IgG on UniProt.org
Related FAQs
- What type of PE do you use in your conjugates?
- We use R-PE in our conjugates.
Customers Also Purchased
Compare Data Across All Formats
This data display is provided for general comparisons between formats.
Your actual data may vary due to variations in samples, target cells, instruments and their settings, staining conditions, and other factors.
If you need assistance with selecting the best format contact our expert technical support team.
 Login / Register
Login / Register 












Follow Us